Original
Fine Art Photography
by
Dr
Larry
A Brechner
National Museum
of the
U.S. Air Force Exhibit
|
|
National Museum |
|||
| Return to Aviation Gallery | Return to Main Gallery | |||
| Photograph | Old Illustrated Postcard Style |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
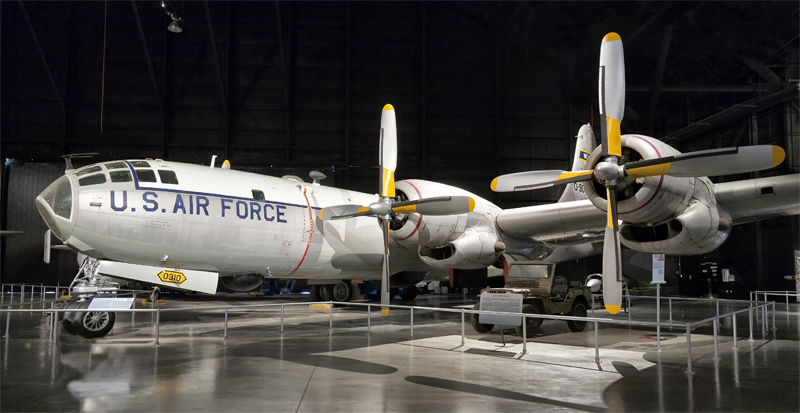 Boeing WB-50D Superfortress #167c |
|
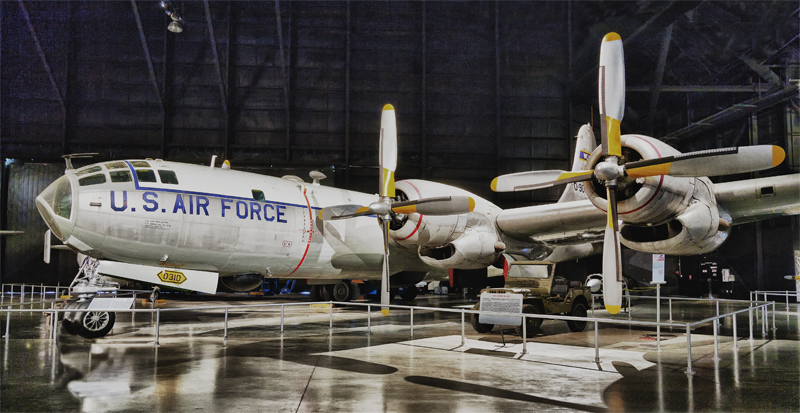 Boeing WB-50D Superfortress #167c (HDR) |
|
|
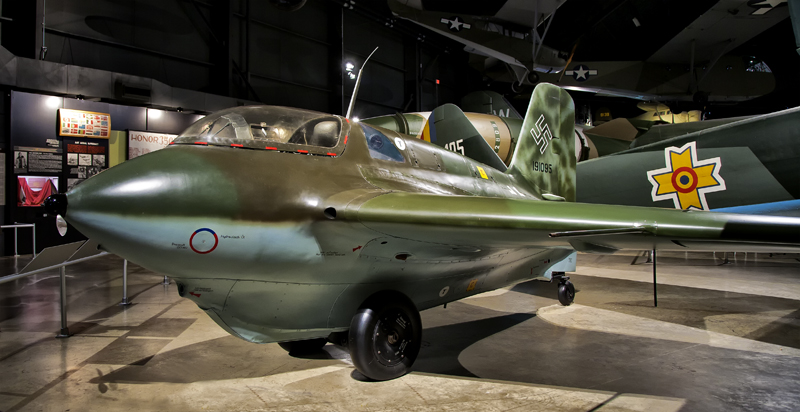 Messerschmitt ME-163 Komet #105c |
|
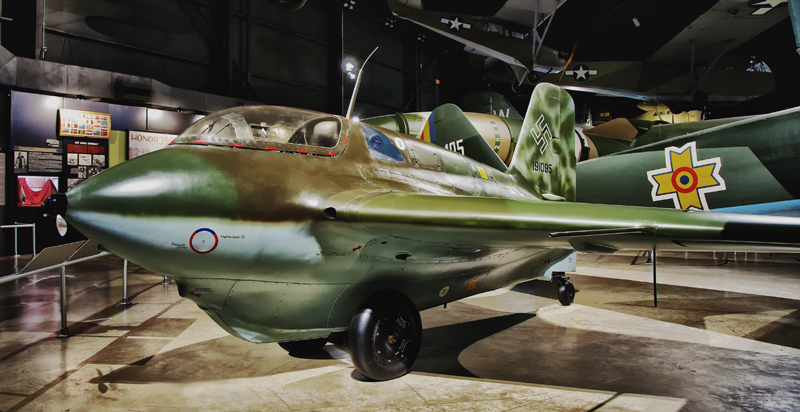 Messerschmitt ME-163 Komet #105c (HDR) |
|
The ME-163B arrived at the museum in 1999. It was restored by the Canadian National Aviation Museum and during that process they discovered what appeared to have been sabotage apparently done by one of the French forced labors that would have eventually caused a fuel tank to rupture and the wing to fail in flight. |
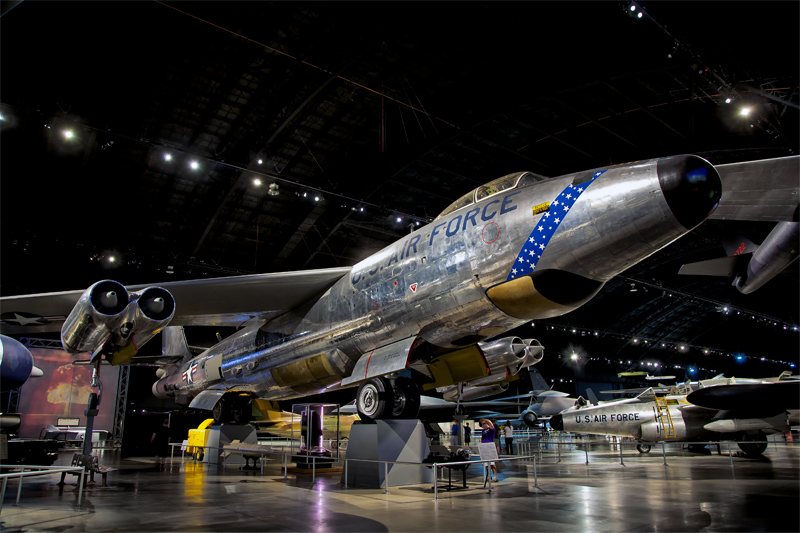 Boeing RB-47H Stratojet #188 |
|
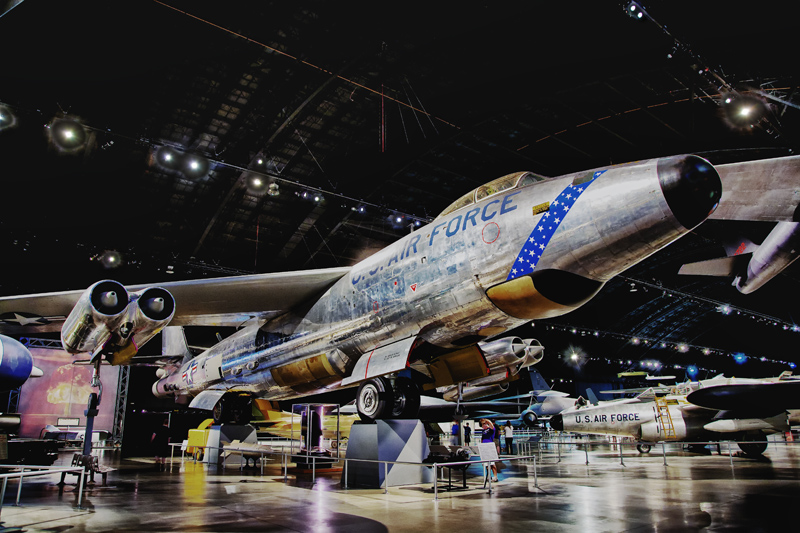 Boeing RB-47H Stratojet #188 (HDR) |
|
|
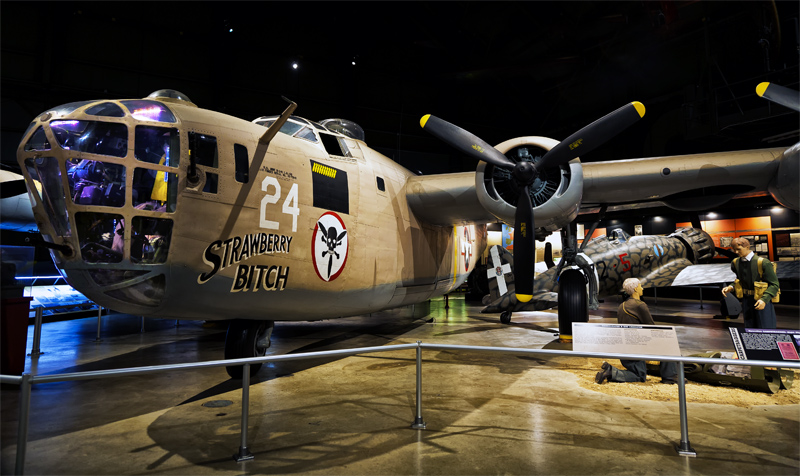 Consolidated B-24D Liberator #88c |
|
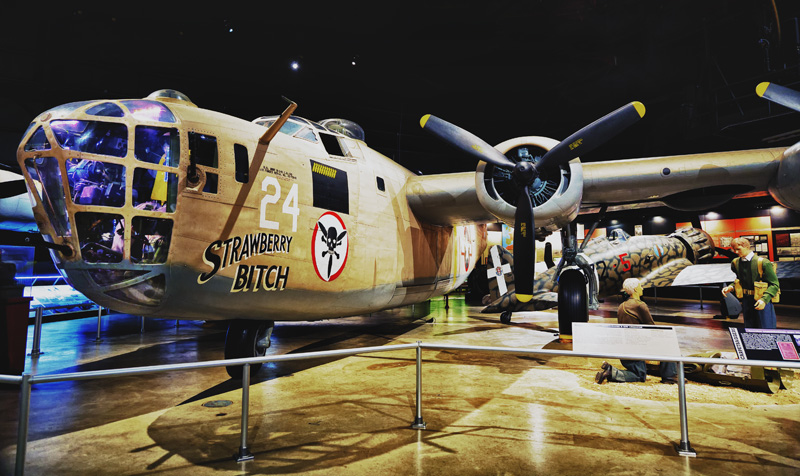 Consolidated B-24D Liberator #88c (HDR) |
|
|
 Convair B-36J Peacemaker #151c |
|
 Convair B-36J Peacemaker #151c (HDR) |
|
|
 Coming Soon |
|
 Coming Soon |
HOME | ARTIST | GALLERY | NEWS | ORDER | CONTACT | LINKS | AWARDS | BRECH.COM
Web Design and
Images © Larry A Brechner - New Perspectives
LAB@brech.com